Androgen dependent zones - areas on the skin with a large accumulation of sebaceous glands (scalp, auricles, face: eyebrows, nasolabial folds, upper third of the chest and back, inner thighs)
Keratolytic agents - these are external medicinal products used for softening and rejection of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, hair, nails for various skin diseases.
Self-regulating means - these are topical medicinal and cosmetic preparations that normalize the function of the sebaceous glands.
Occlusal action helps to reduce transepidermal moisture loss and develops as a result of the application of some forms of external agents.
1.2 Etiology and pathogenesis
The high incidence of diabetes in newborns is due to the presence of large sebaceous glands and an increased level of sebum secretion, comparable to that in adults. These features may be associated with a high content of circulating maternal hormones or increased production of adrenocorticosteroids in early childhood, as well as changes in the biochemical composition of lipids on the skin surface. A number of modern studies have not confirmed the etiopathogenetic significance of the colonization of Malassezia furfur in children with seborrheic dermatitis 5,6,7,8.
The appearance of diabetes in pubertal and older age is due to the high secretory activity of the sebaceous glands, abnormalities in the composition of lipids with a predominance of cholesterol, triglycerides, etc., as well as the significant role of the lipophilic fungus Malassezia 6,7.
The adolescent form of seborrheic dermatitis is often associated with neurological diseases, moreover, the tendency of exacerbations of diabetes after exposure to stress factors has been traced. Frequent recurrences of diabetes in adults can be a skin marker of acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome.
Seasonal fluctuations in temperature and humidity affect the course of the disease, so that exacerbations of diabetes more often occur in the cold season.
1.3 Epidemiology
Children's diabetes and adolescent diabetes are caused by various etiopathogenetic factors.
In children, the disease develops in the first months of life, most often during the first ten weeks 5,6. The prevalence of seborrheic dermatitis in newborns of the first 3 months. life reaches 70% 6.7.
Clinical manifestations of adolescent diabetes mellitus occur in adolescence and older age, more often among males.
1.5 Examples of diagnoses
- Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.
- Seborrheic facial dermatitis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp and face.
- Seborrheic blepharitis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis of the face and torso.
- Seborrheic dermatitis, generalized form.
1.6 Classification
Distinguish children's diabetes and adolescent diabetes.
Children's CD:
- Scalp scalp ("newborn cap"),
- SD torso,
- Leiner-Moussa disease (desquamative erythroderma).
Adolescent BDs:
- Scalp scalp,
- Facial cd
- SD torso,
- Generalized form of diabetes.
2.1 Complaints and history
- When collecting the history and complaints of suspected diabetes of childhood, it is recommended to pay attention to:
- the time of the first symptoms of the disease,
- feeding pattern (breast / artificial),
- the presence of lesions on the skin of the scalp, face, intertriginous areas,
- the presence or absence of itching.
- If you suspect diabetes in adolescents, it is recommended to pay attention to:
- time of appearance of rash (prepubertal / puberty),
- presence of lesions on the skin rich in sebaceous glands (scalp, face, chest, upper third of the back, inner thighs),
- family history (the presence of the above symptoms in close relatives).
2.2. Physical examination
- During a clinical examination in cases of suspected seborrheic dermatitis of childhood, it is recommended to assess the harmony of the physical development of the child, as well as the presence of the main clinical symptoms of diabetes of childhood:
- fat yellow crusts (crusta lactea – milk crust) on the scalp, primarily in the frontal region,
- hyperemia, peeling behind the hairline and behind the auricles,
- erythematous foci, maceration on the skin of the cervical, axillary, inguinal folds,
- itching (from mild to intense), anxiety.
Comments:Childhood diabetes occurs, in most cases, during the first half of life and is characterized by a predominant lesion of the scalp and intertriginous folds.
In diabetes of the scalp, the process most often affects the frontal region, the hair does not fall out, there is little inflammation, and itching is absent.
In diabetes of the trunk, skin folds are involved in the process: cervical, axillary, inguinal, diaper area with a possible damage to the skin of the trunk. The shape of the rash can be ring-shaped, mono-shaped and polycyclic. The location of the elements of a fragmented or confluent character 5,6,11.
- If you suspect erythroderma Leinera Mousse is recommended to assess the presence of:
- sub- or total skin hyperemia,
- peeling,
- anemia,
- diarrhea,
- fever
- weight loss
- lymphadenopathy.
The combination of these symptoms causes a serious general condition.
Comments:in rare cases with diabetes, there is a sudden fusion of foci with the development of sub- or total erythroderma Leiner-Mousse. This pathological condition develops, as a rule, in the first 3 months. life and is considered a complication of seborrheic dermatitis. The etiological factor provoking the complication is unknown, but the sensitizing effect of an opportunistic infection and metabolic disturbances may contribute to the development of the disease.
- If you suspect seborrheic dermatitis in adolescents, it is recommended to evaluate the degree of skin greasiness androgen-dependent zones, as well as the presence of:
- scaly peeling on the scalp,
- infiltrated erythematous foci, layers of oily yellow crusts on skin areas rich in sebaceous glands.
Comments:Adolescent diabetes can occur on the background of the onset of puberty, as well as at an older age. Diabetes is characterized by chronic relapsing course, seasonality of exacerbations. With this form of diabetes, the pathological process is localized in areas rich in sebaceous glands (fronto-parietal region of the head, eyebrows, eyebrow area, nasolabial folds, chest, interscapular region). There is frequent combined damage to the skin of the face and head.
- If generalized diabetes is suspected, it is recommended to assess the presence of yellowish-pink plaques with clear boundaries and flaking on the skin of the body, damage to folds, soak and attachment of secondary infection, which contributes to an increase in the affected area.
Comments:Special forms of a limited version of seborrheic dermatitis are lesions of the external auditory canal and eyelids.
All variants of seborrheic dermatitis may be accompanied by itching ranging from mild to intense.
The algorithm for diagnosing diabetes is presented in Appendix G1.
2.5 Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis of diabetes in children is based on data from the clinical picture. It is carried out with other diseases of the skin of the first year of life, which are characterized by the presence of erythematous foci with symptoms of desquamation.
- Atopic dermatitis has a later onset (8-12 weeks), in most cases there is a family allergic anamnesis, rashes are more often present on the skin of the face, the diaper area is rarely affected, in all cases itching is present.
- Psoriasis in most cases is not typical for this age group. The plaques are intensely hyperemic, have clear boundaries, silvery peeling on the surface. The diaper area may be affected. In a number of supervision the family history is traced. Histological examination is required in doubtful cases.
- Dermatophytosis of smooth skin is characterized by the presence of clearly limited erythematous foci with a peripheral roller. A history of contact with animals. Microscopic analysis with KOH will confirm the presence of a fungal infection.
- Histiocytosis from Langerhans cells is accompanied by a rash on the scalp, body, folds, where the pathological elements can be represented by erythematous papules, small irregular plaques with peeling, covered with yellowish crusts. If you suspect a disease requires histological examination.
The differential algorithm of adolescent diabetes is conducted taking into account the localization of lesions of the skin:
- For psoriatic lesions of the scalp, ears are characterized by more intense hyperemia and infiltration of elements, layering of silvery crusts, positive psoriatic phenomena. Possible damage to the nail plate, the presence of rash of other localizations.
- In atopic dermatitis, an allergic history is traced, rashes on other characteristic areas of the body are determined, there is more intense itching.
- Contact dermatitis is characterized by clear boundaries of foci, which correspond to the area of exposure to an irritant, the absence of characteristic peeling, crusts.
- In the presence of lesions on the skin of the trunk, differential diagnosis is carried out with Ziber's pink lichen, which is characterized by staging the appearance of lesions, the presence of tender peeling in the central part of the plaques.
In the presence of foci in the area of the external auditory canal, a differential diagnosis is carried out with skin lesions of fungal etiology.
In most cases, children's diabetes is resolved independently and does not require inpatient treatment. The choice of treatment tactics for diabetes depends on the degree and severity of clinical manifestations, the duration of the disease, the previous treatment.
3.1 Conservative treatment
Objectives of treatment of uncomplicated diabetes:
- loosening and removing scales and crusts,
- reduction of erythema,
- control of secondary infection.
- With diabetes of the scalp, it was recommended to use keratolytic drugs 1,5,7.
(The strength of the recommendations - III, the reliability of evidence - D)
Comments:- cream with 1-2% salicylic acid w (ATH code D01AE12,
- warm compresses with oils (olive, peach, almond), which are applied to lesions for 40-60 minutes before washing the head.
- After the removal of scales and crusts as anti-inflammatory agents, it is recommended to appoint weak topical corticosteroids 1,3,10.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - C)
Comments:- ointment with 1% hydrocortisone g, VC (ATX code D07AA02), from 2 years old,
cream 0.1% prednisolone aceponate g, VC (ATC code D07AC14), use from the age of 4 months,
cream of 0.1% hydrocortisone 17-butyrate (ATX code D07AB02), used from the age of 6 months,
Application of drugs is carried out 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
- As keratoreguliruyuschih funds, since the neonatal period, it is recommended to appoint a cream containing esters of malic acid, shea butter, shea, glycerin 11,12.
(The strength of the recommendations - IV, the reliability of evidence - D)
- With the defeat of the intertriginous zones, the tactics of treatment are aimed at reducing hyperemia, preventing secondary infection, for this purpose it is recommended to prescribe combined topical agents 5,6,7.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - C)
Comments:cream with hydrocortisone / natamycin / neomycin (ATX code D07CA01), use from birth, up to 1 year - with caution 9,12.
Applications are carried out 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
- In the presence of soak, it is recommended to add solutions of aniline dyes and zinc-containing pastes as antiseptic and adsorbing agents to the treatment, applying them before using topical steroids.
(The strength of the recommendations - V, the reliability of evidence - D)
Comments:extinguishing with aqueous solutions of gentian violet or methylene blue 2 times a day for 5 days,
-application of paste with zinc for 3-5 days.
- In diabetes of the trunk, therapy is also aimed at eliminating the effects of inflammation, preventing secondary infection, for this purpose it is recommended to prescribe combined topical steroids 7,8.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - C)
Comments:cream with hydrocortisone / natamycin / neomycin (ATX code D07CA01) with a frequency of applications 2 times a day for 5-7 days.
- If itching, it is recommended to prescribe antihistamine drugs 5,6.
(Strength of recommendations - III, credibility of evidence - C)
Comments:Dimetinden (ATX code R06AB03) 3-5 drops 3 times a day,
Cetirizine, VC (ATH code R06AE07), 5 drops, 1 time per day from the age of 6 months.
The use of antihistamines is carried out before the elimination of itching.
- In cases of complicated diabetes with the development of sub- or total erythroderma, it is recommended to carry out treatment in a hospital with the use of short courses of hormonal and antibacterial drugs 6,7.
(Strength of recommendations - III, credibility of evidence - C)
Comments:Objectives for treating adolescent diabetes include:
- removal of peeling and erythema in the affected areas,
- reduction of itching
- control of secondary infection.
- With the localization of foci of diabetes on the scalp as a keratolytic, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic agents, it is recommended to prescribe drugs containing salicylic acid and glucocorticosteroids 4,5.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - C)
Comments:lotion with betamethasone dipropionate / salicylic acid (ATX code D07XC01) with a frequency of use 2 times a day for 7-10 days, allowed from the age of 6 months.
- To suppress the possible dissemination of Malassezia mushrooms on the skin of the scalp and on the skin of the body, it is recommended to use shampoos containing antifungal components 11,12,14.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - A)
Comments:Shampoo 2% ketoconazole (ATH code D01AC08), use 2 times a week for 3-4 weeks, then 2 times a month for the prevention of relapse 8,9,12,14.
- shampoo with ciclopirox (ATH code G01AX12), use 2 times a week for 3-4 weeks, then 2 times a month to prevent relapse, use from the age of 10 years.
- As a means of seborrhea, anti-inflammatory, antifungal effects, it is recommended to prescribe drugs with pyrithione-zinc.
(The strength of the recommendations - III, the reliability of evidence - D)
Comments:-1% shampoo, 0,2% pyrithione-zinc aerosol (ATH code D11AX12), allowed from the age of 1 year, use 2 times a week for 2-3 weeks with gradual drug withdrawal.
- With the defeat of the skin of the face, the external auditory canal, the body during the period of acute inflammation, it is recommended to prescribe drugs containing corticosteroids in forms that do not cause an occlusive effect 5,8,11.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - C):
Comments:-cream 0.1% mometasone furoate g, VC (ATX code D07AC13) with a multiplicity of application 1 time per day for 5-10 days, allowed from the age of 2 years,
cream of 0.05% betamethasone dipropionate g, VC (ATX code D07AC01) is used with caution from the age of 6 months, the frequency of use 1 time per day for a period not exceeding 5 days.
- When joining a secondary infection, it is recommended to prescribe a combined means 5,7,8.
(The strength of the recommendations - II, the reliability of the evidence - C)
Comments:- cream with betamethasone / gentamicin / clotrimazole (ATX code D07XC01) is allowed from the age of 2 years, the frequency of use 2 times a day for 5-10 days,
- cream with hydrocortisone / natamycin / neomycin (code ATX CA01) use from birth, up to 1 year - with caution, the frequency of application 2 times a day for 5-10 days,
- After relief of acute inflammation, it is recommended that supportive therapy include:
- cream with 0.2% pyrithione-zinc (ATC code D11AX12) is allowed from the age of 1 year, use 2 times a day for 10-14 days with the gradual cancellation of the drug.
- cream with pimecrolimus (ATH code D11AH02) is allowed from the age of 3 months. Use 1-2 times a day for 10-14 days with gradual drug withdrawal
(Strength of recommendations -III, reliability of evidence - C)
- In the presence of itching, it is recommended to prescribe second-generation antihistamines 1,5,7.
(Strength of recommendations -III, reliability of evidence - C)
Comments:
- cetirizine, VC (ATC code P06AE07) 10 mg once a day for 7-10 days,
- levocetirizine (ATH code R06AE09) 5 mg 1 time per day for 7-10 days,
-loratadine g, VK (ATC code R06AX13) 10 mg 1 time per day for 7-10 days,
-desloratadine (ATC code R06AX27) 5 mg 1 time per day for 7-10 days.
- In severe diabetes mellitus, characterized by a generalized or torpid course of the process, it is recommended to administer antifungal preparations for oral administration 8,11.
(Strength of recommendations -II, credibility of evidence - B)
Comments:- ketoconazole, table. (ATH code J02AB02), allowed from the age of 2 years, children with a body weight of 15-30 kg 100 mg 1 time per day, more than 30 kg - 200 mg per day for 4 weeks 11.14,
- nitraconazole, caps. (ATH code J02AC02) 200 mg once a day for a week, then 200 mg every 2 weeks,
-terbinafin, Table. (ATH code D01BA02), allowed from the age of 2 years, with a body weight of more than 40 kg 250 mg 1 time per day for 4-6 weeks,
- fluconazole, caps. W, VK (ATH code J02AC01), 50 mg 1 time per day for 2 weeks or 300 mg 1 time per week for 2 weeks.
3.3 Other treatments
- Patients with erythroderma Leinera Mousse, together with a gastroenterologist and a nutritionist, are recommended to conduct nutritive therapy to correct gastrointestinal disorders.
(The strength of the recommendations -V, the reliability of evidence - D)
- General recommendations for children with local areas of diabetes include a rational diet of the child and mother. In adolescent diabetes, it is recommended to observe a rational diet with the restriction of extra active substances, to exclude the use of aggressive detergents, wearing synthetic clothing.
(The strength of the recommendations -V, the reliability of evidence - D)
- It is recommended to maintain a favorable psycho-emotional background with the exclusion of stressful trigger factors.
(The strength of the recommendations -V, the reliability of evidence - D)
- When the skin of the trunk and intertriginous zones are affected, air baths are recommended, bathing in warm water with the use of cosmetic oils.
(The strength of the recommendations -V, the reliability of evidence - D)
5. Prevention and follow-up
Most patients with pediatric and adolescent diabetes receive therapy in outpatient settings. In the case of generalization of the skin process, severe condition in children of the first year of life, the development of Leyner erythroderma, inpatient treatment is indicated.
The duration of hospital stay may be on average 10-14 days.
Criteria for assessing the quality of care
Table 1 - Organizational and technical conditions of medical care.
Type of medical care
Specialized medical care
Terms of care
Inpatient / day care
Form of medical care
table 2 - Criteria for the quality of care
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
The main reasons for the development of seborrheic dermatitis in children are not fully understood, but today the proven fact is the presence of the causative agent of this pathological condition - the fungi Malassezia furfur. They are considered conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, which are activated in the presence of favorable conditions for their reproduction.
The main precipitating factors of seborrhea in infants and young children are divided into two groups: internal and external.
- hormonal imbalance, a surplus of hormones in the baby’s blood, endocrine pathologies,
- stress or illness of the nervous system,
- reduced immunity
- lack of biotin (vitamin B group) that regulates the metabolism and metabolic processes in the body.
- familial predisposition
- violation of the sweat and sebaceous glands, changing their formation in the prenatal period,
- unfavorable environmental situation
- shampoo shampoos containing alkali.
Clinical manifestations of seborrhea in children
The first symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis in infants appear between 2 and 3 weeks after birth.. They are associated with an excess of hormones in the blood of a newborn that enter the body through breast milk, as well as with the beginning of the active functioning of the sebaceous glands.
First, elements of the rash are observed on the scalp in the form of small patches of redness, covered with white or yellowish oily scales. Then the rash turns into gneiss. It is formed from peeling epithelial cells and sebum and covers certain areas of the scalp and eyebrows in the form of unevenly layered crusts of various thicknesses. Also, seborrheic lesions may appear in the natural folds, on the wings of the nose, in the armpits.
When the first signs of seborrheic dermatitis appear in children, you should immediately contact a specialist - pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist.
Principles of treatment of pathology by various means
adrotate banner = ”4 ″ Seborrheic dermatitis in childhood is a complex, but not dangerous disease, which, with proper care and hygiene, passes on its own within a few weeks. In this case, it is impossible to self-medicate - manifestations of seborrhea in children can be confused with other ailments, therefore it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, and the treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a physician.
Therapy for seborrheic dermatitis is based on an integrated approach and includes:
- washing the baby’s head with special hypoallergenic shampoos (Skin - Cap, Mustel Bebe shampoo, Ionel), which reduce the activity of fungi and reduce the inflammation of the skin,
- gentle removal of gneiss with a soft brush or special comb,
- hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers, correct weighted introduction of complementary foods,
- the use of drugs (antifungal agents, local hormone ointments and antibiotics when attaching a bacterial infection),
- folk remedies for the treatment of various forms of seborrheic dermatitis (decoctions of herbs for rubbing into the scalp, applications of soda, sea salt and other healing compositions, essential oils and ointments).
Therapy of seborrheic dermatitis in children folk remedies
For the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children, folk remedies use essential oils and medicinal plants with anti-inflammatory, drying, soothing and disinfecting effects:
- chamomile and calendula flowers,

- leaves of sage, nettle, yarrow and plantain,
- Oak bark,
- tansy flowers,
- special blends of herbs and essential oils (tea tree, eucalyptus and lavender).
The use of folk remedies in infants
The skin of the scalp of newborns and young children have certain anatomical and functional features:
- vulnerability,
- special structure of the epidermis,
- active blood supply.
Therefore, not all traditional medicine can be used in infants. For the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children under one year of use:
- decoction of chamomile (two tablespoons of flowers should be poured with a liter of boiling water, left for half an hour) - used to rinse the baby’s head after washing with a special shampoo or applied as lotions after combing the seborrheic crusts,
- an infusion of tansy flowers: one hundred grams of flowers should be poured with a liter of boiling water and let it brew for 30-40 minutes - used to rinse the scalp after washing,
 decoction of nettle or sage (100 grams of dry raw materials pour 1.5 liters of boiled water, boil in a water bath for 10 minutes, insist for 20 minutes) - used for washing or rinsing the head.
decoction of nettle or sage (100 grams of dry raw materials pour 1.5 liters of boiled water, boil in a water bath for 10 minutes, insist for 20 minutes) - used for washing or rinsing the head.
Essential oils in this age are used with extreme caution, only as directed by a physician.
Before combing the gneiss, the baby's head is smeared with fatty baby cream, almond or olive oil or petroleum jelly. They put a hat on and after 20-30 minutes they comb out the areas of the gneiss with a special brush. After the procedure, lotions from the bark of the oak or collecting herbs (sage, chamomile, calendula and nettle) are effective..
The main forms of seborrhea and symptoms of the disease
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin disease caused by fungal bacteria of the Malassezia genus. Seborrhea in children can occur in any of the forms: mild, moderate or severe.
- The mild form is characterized by redness of the scalp, and sometimes the appearance of scales.
- The average form manifests the spread of peeling and redness on the body and limbs of the baby. Skin rashes may appear
- Severe form is associated with the spread of scaly areas on the face, shoulders, torso and ears.

At the beginning of the disease, redness appears on the head of the child, which can gradually peel off.
Over time, the baby becomes restless, there are problems in the intestines.
In severe infant seborrhea in newborns, the following symptoms occur:
- worsening sleep
- anxiety,
- vomiting
- lack of appetite,
- lethargy.
Treatment of symptoms should begin with the removal of the root cause.
Folk remedies for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in adolescents
The main reason for the occurrence of seborrhea symptoms in adolescents is the hormonal alteration of the body and the disruption of the normal functioning of the sebaceous and sweat glands. Therefore, therapy is aimed at improving metabolic processes in the body and reducing skin inflammation.
Herbal preparations are widely used for the treatment of this form of the disease, in particular, herbs for local use (washing, rinsing the scalp, lotions, rubbing, masks):
- golden mustache juice,
- decoction of burdock, sage and oak bark,
- infusion of Hypericum,
- decoction of tansy flowers.
 Be sure to enrich the child's diet with foods containing vitamins and minerals:
Be sure to enrich the child's diet with foods containing vitamins and minerals:
It is recommended to use special healing compositions for rubbing into the skin of the scalp:
- camphor alcohol, vinegar and aloe juice,
- sea salt dissolved in a small amount of water
- tea fungus infusion
- tea tree, lavender and eucalyptus essential oils with antifungal activity,
- a special ointment of golden whisker juice (1 tbsp. spoon), valerian tinctures (1 tbsp. spoon) and baby cream with olive oil, 1 tbsp. spoon rubbed into the scalp every other day for 3 hours, the treatment is 2-3 weeks.
To normalize the metabolism take a decoction of currant bark, extract of hypericum and yarrow.
It is important to remember that all these tools are part of a comprehensive treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and are prescribed by a doctor.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis in children
Of course, not every child suffers from seborrheic dermatitis. The disease occurs for the following reasons:
- If the baby still has hormones of the mother in the body, which he accumulated during his stay in her stomach. A large number of hormones provokes the activity of the sebaceous glands. Gentle skin begins to become covered with crusts and redness.
- Hereditary predisposition, characterized by allergic reactions to infections, improper functioning of the digestive tract, dysbacteriosis. Why sebaceous glands work more actively.
- Infection with the fungus Malasseriafurfur. With reduced immunity, the fungi multiply rapidly. Getting rid of them can be extremely difficult.
If the disease is mild and there are no complications, it can go away on its own. However, there are cases when seborrheic dermatitis in children progresses and lasts up to several years. This form needs treatment.
As for dermatitis in older children, it is important to determine the cause of the disease. After all, a therapeutic course is aimed at eliminating a specific factor. Causes of inflammation of the skin on the head may be:
- lack of proper child care,
- living near an industrial or metallurgical enterprise, a factory polluting the environment with chemical waste, a large accumulation of exhaust gases,
- previously incorrectly chosen medicines for the treatment of dermatitis in a child,
- hit on the scalp coloring matter.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
 Symptoms of the disease in children are determined by such points:
Symptoms of the disease in children are determined by such points:
- crusts on the head cause itching, causing the baby to become moody and often crying,
- when the fungus joins, the skin is covered with reddish patches with plaques (plaques differ in even borders, formations are formed by combining into one whole the nodules covered with scales),
- if the disease develops, the plaques turn into a garland-like structure that surrounds the head of the child,
- behind the ears, seborrheic dermatitis takes on the form of sticky scales and weeping cracks,
- skin flakes, at the beginning of the hair a lot of yellow blotches resembling dandruff.
If you do not treat the skin in this case, the baby may lose all the hair on the head. The affected areas swell, there is a risk of infection with a secondary infection. Suppuration is possible. The child becomes sluggish, loses his appetite, worries, the body weight gradually decreases.
Clinical forms
 According to the nature of the inflammatory processes, 4 forms of seborrheic dermatitis are distinguished.
According to the nature of the inflammatory processes, 4 forms of seborrheic dermatitis are distinguished.
- Oily. Accompanied by increased activity of the sebaceous glands, the formation on the scalp of large lamellar scales, which, merging, form extensive foci. The greasy secret becomes a favorable environment for the development of bacteria, so inflammation may be complicated by infection.
- Dry It is characterized by reduced secretion of sebum, the formation of grayish or yellow-white scales covering the entire surface of the head (easily removed when combing). At the same time the hair is thinning, they become brittle, start to fall out. It is the dry form of seborrhea that most often occurs in infants.
- Mixed Combined form of pathology in which dry seborrhea can develop on the head, and oily seborrheic dermatitis on the skin of the face.
- Physiological. Most often develops in adolescence due to hormonal adjustment. In this case, the consequence of dysfunction of the sebaceous glands is acne.
Often, seborrheic dermatitis on the head of a child develops in 2-3 weeks after birth. Foci of seborrhea affect the head, may also appear in the skin folds. According to the severity of clinical symptoms, there are 3 degrees of seborrhea in a child.
- Mild - foci of inflammation are localized on the head, rarely affect the skin on the forehead, cheeks, behind the ears. At the same time, the general condition of the child does not deteriorate.
- Medium - inflamed lesions spread to the skin of the trunk and extremities. Dermatological signs are complemented by common symptoms: digestive disorders (diarrhea, frequent regurgitation), emotional arousal.
- Heavy - in pathological processes involved ⅔ of the total area of the skin. The affected areas redden, swell, and are complicated by secondary infection. Moisture and suppuration of the inflamed foci develop.The child's appetite is deteriorating, body weight is decreasing, diarrhea is constantly present. He becomes sluggish, restless, does not sleep well.
Secondary infection of the skin can lead to the development of blepharitis, otitis, pyoderma and other bacterial complications.
 For the treatment of infants, as a rule, it is sufficient to use special shampoos and gently comb the crusts with the help of a baby comb. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected in an older child, then additional diagnostics (blood tests, ultrasound of the digestive system and the thyroid gland, bacteriological studies) are necessary to identify the exact cause of the disease. If necessary, the doctor sends the child to consult a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist.
For the treatment of infants, as a rule, it is sufficient to use special shampoos and gently comb the crusts with the help of a baby comb. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected in an older child, then additional diagnostics (blood tests, ultrasound of the digestive system and the thyroid gland, bacteriological studies) are necessary to identify the exact cause of the disease. If necessary, the doctor sends the child to consult a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist.
After determining the causes and making an accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed: seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in children lends itself well to drug therapy, subject to the doctor’s recommendations, taking preventive measures to care for the scalp, and organizing dietary nutrition for the child.
 Drug treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children begins with the use of special pharmacological shampoos:
Drug treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children begins with the use of special pharmacological shampoos:
- Nizoral - ketoconazole-based shampoo has antifungal effect, is active against microorganisms that cause the development of seborrheic dermatitis. The drug effectively eliminates peeling and itching, has no age restrictions. Can be used for shampooing for the purpose of treatment (twice a week for 15-30 days) or prevention of relapse (once a week for a month).
- Ionel - a structural analogue of Nizoral based on ketoconazole exhibits antifungal properties, reduces burning and itching of the scalp, redness and peeling. It is applied twice a week. The full treatment course is from 2 to 4 weeks.
- Skin Cap - shampoo based on zinc pyrithionate exhibits antifungal and antibacterial activity, inhibits the processes of excessively active cell division. The remedy reduces inflammation and symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. Used to wash hair 2-3 times a week for 14 days. Appointed to children older than a year.
- Tsinovit - the combined shampoo based on pyrithione zinc, dexpanthenol, climbazole has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antifungal, sebiostatic and regenerating effects. It is applied 2-3 times a week during the month. Appointed to children from the 1st year of life.
In addition to shampoos, for the treatment of seborrhea may prescribe sulfur ointment. The deposited sulfur, which is part of the product, has an antiseptic, disinfecting, antimicrobial and antiparasitic effect. However, the ointment is very irritating to the skin, therefore it is contraindicated in children under 3 years old.
 If, after a course of treatment with shampoos and ointments, it is not possible to cure seborrheic dermatitis in a child, the doctor may prescribe hormonal external agents. If seborrhea is complicated by pyoderma, ointment with antibiotics is also prescribed. Preparations are selected in each case individually, taking into account the severity of the pathology and the age of the baby.
If, after a course of treatment with shampoos and ointments, it is not possible to cure seborrheic dermatitis in a child, the doctor may prescribe hormonal external agents. If seborrhea is complicated by pyoderma, ointment with antibiotics is also prescribed. Preparations are selected in each case individually, taking into account the severity of the pathology and the age of the baby.
Simultaneously with the treatment of dermatological manifestations of seborrhea, therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating the underlying cause of the pathology. Assign:
- sedatives (based on valerian, lemon balm, motherwort and other soothing herbs),
- preparations for the restoration of intestinal flora (Acilact, Hilak Forte),
- immunostimulating drugs (Viferon, Derinat),
- vitamin complexes (Pikovit, Alphabet, Aevit).
Folk remedies
 For the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in a child, along with drug therapy, you can use traditional remedies:
For the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in a child, along with drug therapy, you can use traditional remedies:
- infusion of oak bark (helps to reduce the appearance of oily form of seborrhea, rubbed into the skin every other day),
- infusion of collecting plantain, calendula, chamomile (rubbed every morning into inflamed foci),
- olive or almond oil (applied to lesions 20 minutes before washing the head, softens crusts, facilitates their removal),
- laundry soap (used for shampooing in children over 5 years old),
- infusion of sage or chamomile (used as a lotion).
It is important to understand that the use of folk remedies is an auxiliary method of treatment and does not cancel the main drug therapy.
Along with prescribing medications and hygienic care recommendations, pediatricians develop a diet for young patients, based on the consumption of foods high in vitamins A, C, B, zinc, and selenium by a child or nursing mother. It is important to prevent overdose of these compounds, otherwise the inflammatory processes may be aggravated.
During and after the end of therapy, doctors, including the famous pediatrician EO. Komarovsky, recommend organizing a proper diet for the child and nursing mother: eliminate allergy foods from the diet (strawberries, citrus fruits, honey, nuts, mushrooms, seafood), flour, sweet, fatty, preserved and pickled.
 With seborrheic dermatitis, the basis of the daily diet of a child or a nursing mother should be:
With seborrheic dermatitis, the basis of the daily diet of a child or a nursing mother should be:
- dairy products,
- low-fat varieties of fish, meat,
- vegetables, fruits and berries (except allergenic),
- cereals,
- chicken eggs,
- dishes based on gelatin (jelly, jellied),
- Rye bread,
- vegetable oils (olive, sunflower, linseed).
All dishes are recommended to stew, bake or steam. Fried from the diet is also completely excluded.
Causes of the disease
Seborrheic dermatitis can occur in children for various reasons, often the disease contribute to:
- genetic predisposition
- hormonal disbalance,
- infectious and chronic diseases,
- impaired gastrointestinal activity,
- poor hygiene, poor care,
- taking drugs that negatively affect the immune system
- stress,
- poorly selected cosmetics.
The main "culprit" of seborrheic dermatitis is the fungus Malassezia furfur. Yeast-like fungi live in almost every human body, but their activation occurs under favorable conditions for them, such as reduced immunity or changes in the acidity of the skin.

Types and clinical symptoms of the disease
Seborrhea on the head of a child is of several types: oily, dry and mixed. The development of a certain type of seborrhea depends on various factors and is also manifested in each case in different ways:
- Oily form. Occurs due to the increased functionality of the sebaceous glands in the child. This form is characterized by the appearance of large scales, which tend to merge into one continuous spot. Due to the large amount of fat on the head, various infectious processes can occur. With the manifestation of oily seborrhea in adolescence at the same time, acne can occur. Read more about the treatment of this type of seborrhea in this article.
- Dry seborrhea. In the case of the slow functioning of the sebaceous glands, a dry form of seborrhea may occur on the children's head. This type mainly appears in young children. In this case, the scales have a gray-white or yellow-white color. Dry dermatitis threatens with thinning and brittle hair, small hairline can also appear. More about this type here.
- Mixed look. The mixed form of the disease is characterized by the presence of both oily and dry scales. Often dryness is observed on the head, and fatty areas appear on the skin of the face.
Treatment of seborrhea in children
First of all, it is necessary to accurately diagnose and find out the cause of skin manifestations. It is not always necessary to use various means, in some cases, seborrhea passes on its own.
Important! Sometimes parents resort to folk remedies for the treatment of seborrhea. They do not always have a positive effect and even can hurt. It is not worth risking the health of the child.
For the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in children used external means. In the presence of yellow crusts in small children, in light cases, it is enough just to use special shampoos for bathing, and then gently comb the crusts with a baby comb.
In other cases, it is recommended complex therapy with:
- medicinal preparations in the form of ointments and creams,
- physiotherapy,
- specialized shampoos and other cosmetics,
- special diet.
Such a phenomenon as dermatitis in children should not be ignored and wait for it to pass, otherwise you can start the condition. It is also not recommended to independently choose a remedy and, especially, to resort to traditional medicine without prior consultation with a specialist.
Treatment will not be correct without a special diet. It is imperative to exclude from the diet: fatty, flour and spicy foods, sweets, fast food, canned food, smoked meats, marinades, snacks, sauces and sweet sparkling water.
Also, in some cases, it is necessary to abandon products that can cause an allergic reaction: honey, nuts, mushrooms, citrus fruits, seafood and so on.
Both an adult and a child with dermatitis should include the following foods in their diet:
- lean meat: chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal,
- vegetables, fruits and berries that are not a potential allergen,
- croup: buckwheat, oatmeal, barley,
- Rye bread,
- oils: olive, sunflower, linseed and others,
- lean fish, if the child has no reaction to it,
- Milk: kefir, sour cream and yogurt,
- chicken eggs.

Vitamins can also help prevent the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Fish oil, vitamins A, E and B are particularly helpful in protecting against seborrhea.
Vitamin complexes are perfect: Pikovit, VitaMishki, Alphabet, Aevit and others. Before use, be sure to consult your doctor.

Ointments and creams
In case of dermatitis in a child, in most cases, non-hormonal agents are prescribed, which are sorbing, antiallergic, cosmetic, immunostimulating, etc. The only negative - non-hormonal therapy usually lasts longer than in the case of the use of hormonal drugs.
Parents mainly use zinc-based products, as well as ichthyol ointment. In addition, from pharmacies it is worth noting the following:
- La Cree ointment - will help get rid of redness, peeling and itching, applied from birth,
- synthomycin ointment - antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent containing an antibiotic, allowed to use after 1 year,
- Bepantin - a safe means of promoting rapid cell repair, is used even in newborns.
In a situation where the use of hormone-containing products is not avoided, there will also be plenty to choose from. In particularly advanced cases, it is these drugs that will help to quickly get rid of the symptoms and alleviate the condition of the child. It is important to choose the right drug and use it only for a short period of time.

In the case of hormonal therapy, it should be noted that up to 7 years the remedy is prescribed exclusively by a doctor! For newborns and infants hormone ointments and creams are not used.
Among the effective drugs worth noting:
- Hydrocortisone is a popular ointment widely used in pediatric therapy,
- Advantan - contains methylprednisolone in composition and is used on any part of the skin in children after six months,
- Flutsinar - the active ingredient is flutionol acetonide, up to two years is contraindicated.
It is important to carefully select an ointment or cream with hormones, since they all have a number of contraindications and possible side effects. In this regard, self-treatment is not recommended!
Cosmetics
Ordinary shampoos can cause even greater irritation in the child, so it is recommended to use special products to wash hair and scalp with a gentle composition:
- Froderm Shampoo,
- Psoryl,
- Mustela Bebe.

For babies under two years old, well-known companies produce a separate line of shampoos. Typically, the composition is not much different from the version for adults, the difference is only in the concentration of active ingredients.
What is seborrhea of the scalp in a child
 In children, seborrhea of the scalp is manifested in the form of peeling and unpleasant itching. This condition is caused by malfunction of the sebaceous glands. If little sebum is secreted, dandruff is white.
In children, seborrhea of the scalp is manifested in the form of peeling and unpleasant itching. This condition is caused by malfunction of the sebaceous glands. If little sebum is secreted, dandruff is white.
In case of excessive secretion, the horny particles stick together and acquire a yellow tint.
Scalding on the scalp is called seborrheic dermatitis (seborrhea in Greek means "flow"). It is believed that its causative agent is a fungus, which begins to multiply actively in case of violation of the skin lipid balance.
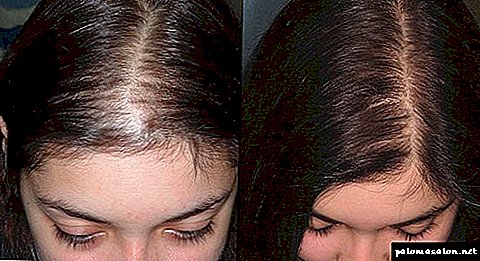
The following photo of the child shows what seborrheic dermatitis or “milky crusts” look like in infants.
Types and symptoms of seborrhea
There are several forms of the disease:
- Dry Associated with poor performance of the sebaceous glands. As a rule, such seborrhea occurs in newborns. Manifested in the form of yellow or light gray scales.
- Oily. On the contrary, is associated with excessive secretion of sebum. The head takes on a shiny, neglected look. Scales begin to stick together among themselves, filling the increasing part of a surface of a skin.
- Mixed Some areas have a sign of dry skin, while others appear as massive flakes. Occurs at any age.
In order to properly implement the treatment, mothers should be guided by the symptoms of the manifestation of the disease.
 Signs of dermatitis in a child are:
Signs of dermatitis in a child are:
- the formation of scales of yellow, white or grayish color mainly in the parietal part of the head and on the crown,
- the presence of seborrheic crusts in other areas of the skin of children, for example, on the eyebrows, neck, behind the ears (in infants, the transition of seborrhea to the armpits, groin, buttocks is possible)
- there is no too pronounced inflammation (when you remove the crusts, the skin will have a healthy, possibly slightly pinkish color),
- peeling does not bring much discomfort to the child, especially if it is “milky” crusts in babies,
- severe hair loss
- in some cases - excessive sweating of the hands, feet and in the armpits.
Sometimes the surface of the skin begins to acquire relief, becoming covered with tubercles. Such areas are called seborrheic elements or zones. Often, they are located on the face, eyebrows, scalp.
It happens that some seborrheic elements are localized on the back - in its upper half.
Atopic dermatitis, unlike seborrheic, is manifested by a more pronounced clinical picture with severe inflammation, itching and even small blisters. It is an allergic reaction to food or individual accessories, wardrobe items. During severe allergies, fever may occur.
An important point! Want to check the skin of the baby? Take a sanitary napkin and wipe the face with it, especially the creases of the nose. Make sure that the child has not used cosmetics - lotions, skin gels, etc. If there are traces on the napkin, then the child has an increased sebum secretion.
Seborrhea in infants on the head
 Unpleasant crusts in newborn babies of the mother can be seen already in the second week of the baby’s life. Scales are especially active in the first 3 months, when the formation of all body systems of the body occurs. As a rule, they disappear closer to the year, but can linger up to 2-4 years.
Unpleasant crusts in newborn babies of the mother can be seen already in the second week of the baby’s life. Scales are especially active in the first 3 months, when the formation of all body systems of the body occurs. As a rule, they disappear closer to the year, but can linger up to 2-4 years.
On the scalp and skin of 50% of babies dermatitis is found. Over time, it passes, but the scales must be removed mechanically.
If we talk about the causes of this phenomenon, they have not been thoroughly studied. Doctors believe that seborrhea in newborns appears due to:
- hormonal restructuring (as is known, after birth, babies hatch, which he picked up from the mother during fetal development - the hormonal background, characterized by malfunctions in the sebaceous glands, is becoming established)
- external factors (frequent stay in a hat, bathing in shampoos, feeding a nursing mother, artificial mixtures and early introduction of complementary foods),
- reproduction of the fungus Malassezia furfur, which dwells on the scalp and leads to the formation of dandruff,
- weakened immunity (infections, low weight, genetic predisposition can be the causes of the disease),
- violations of thermoregulation processes, which is typical for children under one year old (due to frequent baby wraps, there is a failure in thermoregulation, which affects the sebaceous glands).
Children's dermatitis in adolescents
Adolescence is an unforgettable and impressive page of the life of every person. At this time, children are trying to stand out from the crowd, because there is a formation of their own "I". They truly fall in love for the first time and want to be as attractive as possible. But here, due to certain circumstances, rashes, flaking on the skin and ill-fated dandruff significantly spoil the picture.
If seborrheic dermatitis before the age of one year affects the scalp regardless of gender, then in adolescents girls suffer mainly from the disease.
In adolescence, as you know, hormonal changes in the body occur. That is why on the skin you can see black spots (eels, comedones), peeling, and dandruff on the hair.
 Other causes of dermatitis:
Other causes of dermatitis:
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (dysbiosis leads to disruption of metabolic processes, which, in turn, affect the production of a secret - occurs in children 5-12 years old, may be in adolescents due to improper diet),
- frequent stresses (“flimsy” psychoemotional state entails violations in the sebaceous glands, because it is noticed that children in adolescence try to stand out in a circle of peers, but not always successfully, or experience undivided love - because of this frequent disorder),
- Malassezia furfur fungi, which usually develop on the scalp, causing dandruff (13-16 years),
- unbalanced nutrition (if sweets and flour are frequent guests in the baby’s ration, then the fungi on the skin, fed by such products, begin to feel great, and the lack of vitamin A and E directly contributes to the sebaceous gland dysfunction),
- frequent use of alcohol-based cosmetics (as you know, adolescents actively rub their skin with lotions, not thinking about their composition),
- wrong selection of shampoo (if you do not take into account the type of scalp, then you can only worsen its condition),
- Frequent exposure to the sun or hypothermia in the winter affects the skin condition negatively (girls and teenage boys very often refuse to wear hats and then suffer unpleasant manifestations on the skin).
An important point! Sometimes teenage girls use concealer to hide the unpleasant manifestations of seborrhea. It is strictly forbidden to do this, because due to the closure of the pores, the problem only gets worse.
Features of treatment
 Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in a child is not fatal. But due to the confluence of certain circumstances possible complications of the disease, which manifests itself in the form:
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in a child is not fatal. But due to the confluence of certain circumstances possible complications of the disease, which manifests itself in the form:
- the strongest itch, provoking the desire of the baby to comb the skin to the blood,
- spreading scales protruding the scalp,
- severe redness of the dermis at the site of peeling,
- infection with streptococci and staphylococci, which appear due to the spread of inflammatory processes.
Therefore, to prevent such complications, you need to start the right treatment as early as possible.
Before you engage in the treatment of seborrhea, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist. The doctor of a narrow focus will conduct a visual diagnosis of the disease, as well as prescribe skin tests for the presence of fungus and biochemical blood tests for hormones. In rare cases, ultrasound of the thyroid gland and abdominal cavity. Only after properly diagnosed, you can quickly and easily get rid of dermatitis.
In no case can not be applied to the seborrheic areas of baby soap, because it still dries the skin. For babies it is forbidden to use shampoos for adults, - only special baby shampoo is suitable for their skin.
Seborrheic dermatitis can be confused with atopic psoriasis, eczema, and even rickets. Therefore, the only right decision - a trip to a dermatologist.
Pharmacy Treatment
Another treatment option is a trip to a pharmacy, where a pharmacist will select a remedy for removing peeling and treating dermatitis.
 Among pharmacy drugs use:
Among pharmacy drugs use:
- cleansing oils of jojoba, olive, peach, almond, which will soften the scales for the purpose of further mechanical removal,
- creams, gels, foams, lotions, are also designed to combat the elimination of flakes and pore cleansing (they are applied overnight, and simply washed off in the morning, cosmetics fight against seborrhea, locally regulates the secretion of sebaceous glands, the most effective means of the French DS Uriage brands, Mustela Stelaker),
- medicinal creams (applied several times a day and not washed off, aimed at combating microbes and stabilizing the sebaceous glands, the most popular means of Bioderma Sensibio DS +, Saforel, which can be used for babies' skin),
- antiseborrheic shampoos (they are aimed at fighting the fungus and restoring the lipid balance - for example, Friderm, Nizoral, Sebosol, Sulsen) and tar soap,
- topical zinc preparations that will dry the scalp, salicylic acid and sulfuric ointment,
- means for internal use (bifonazol, ketoconazole), the acquisition of which is recommended in case of detection of the fungus.
All these drugs do not have a lightning effect. It should take 1-2 months for you to notice an improvement.
Important! If your child has atopic dermatitis, you cannot do without special antifungal ointments. As a rule, prescribe ointments, which include betamethasone, clobetasol and hydrocortisone.
Treatment of folk remedies
 Very well in the fight against dandruff will help decoctions based on healing herbs:
Very well in the fight against dandruff will help decoctions based on healing herbs:
When bathing a baby, be sure to add a brewed string to the tub, hop cones, and oak bark.
To eliminate dandruff, prepare decoction based on hypericum, burdock roots and nine-strength. Mix the crushed ingredients in equal proportions and boil on the fire for 20 minutes. After the infusion is infused, strain through a sieve and begin to rub into the scalp. Close the hair with a plastic hat and wrap with a towel.
For a child of 5 years old, it is recommended to rub castor oil, fresh aloe juice and egg yolk into the scalp.
Teenagers can try quite a powerful tool in the fight against peeling: combine in equal proportions the juice of onions, vodka and castor oil. An hour before water procedures, rub into the scalp and face.
If you want to significantly soften the crusts, You can make a special ointment. ABOUTcooking properties:
- combine crushed leaves of plantain, flowers of Hypericum and calendula,
- boil them over the fire so that the mixture is halved
- add some vaseline or unsalted butter,
- rub into the scalp regularly until the symptoms are completely eliminated.
Use fresh parsley to eliminate seborrhea. Chop about 3 tbsp. l greens and fill it with a glass of boiling water. Let it stand for half an hour and you can start rinsing the scalp. The course of treatment is at least a month.
Alternative treatment
Alternative treatment is reduced to the mechanical removal of crusts, which are pre-impregnated with oils in order to soften them.
 To remove the "milk crusts" from the baby, follow these guidelines:
To remove the "milk crusts" from the baby, follow these guidelines:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before the procedure.
- An hour before bathing, rub normal baby oil into your scalp - it should be warm.
- Now tie a warm cap and you can play with the baby.
- Immediately before bathing, the cap is removed and the peeling is removed with a plastic comb with fine teeth. Try to comb the scales comb, keeping it at an angle of 30-40 degrees.
- Now you can start swimming.
- After the water treatment, once again walk the ridge, because the head of the crumbs is well steamed.
Attention! Performing such manipulations is prohibited to rip off the skin with nails or peel dandruff on dry, because you can significantly injure the delicate skin of the baby and cause an infection.
Unfortunately, mechanical removal of crusts does not always lead to the desired results. Must undergo at least 2-3 procedures to eliminate the scales. In addition, very often a new crust reappears on the head of hair, because the root cause has not been eliminated.
Also You can try sea salt. Prepare from it a solution for washing the curls after the main wash.
Instead of shampoo, it is recommended to use 2 times a month. diluted mustard powder (only for children from 13 years).
To remove the fungus that lives on the scalp, rinse it with the usual water with vinegar or salicylic acid.
If the young man used to wash his hair with soap, it is better to replace it with tar remedy.
To relieve itching, you can use lemon juice diluted with water.
Disease prevention
 As a rule, seborrheic dermatitis with the pubertal period goes away. But so that he does not appear again, you need to follow these recommendations:
As a rule, seborrheic dermatitis with the pubertal period goes away. But so that he does not appear again, you need to follow these recommendations:
- observe the day regimen (exclude excessive physical exertion, watch the duration of the night's sleep - at least 8 hours, and for small children plus a couple more hours during the day),
- restore the diet (sweets and muffins need to be limited; instead, enter fresh fruits and vegetables, be sure to consume 40 grams of protein (meat or cheese, you can use beans) for each meal,)
- make it a rule to take multivitamin complexes (in the pharmacy you will find plenty of vitamin A for children, make sure that they contain vitamin B, which normalizes the work of the sebaceous glands),
- review baby cosmetics (exclude alcohol-based lotions, pick up creams and shampoos depending on skin type),
- Be sure to cure all pathologies that can lead to skin lipid imbalance,
- in case of severe nervous breakdowns and frustration, record the child at the reception to a neuropathologist or psychologist,
- strengthen the immune system (proper nutrition, healthy sleep, walks in the fresh air, moderate exercise, sunbathing),
- regularly care for the skin (it is advisable to choose cosmetics after consulting with a dermatologist).
If you are going to get rid of seborrheic dermatitis for a long time, it is forbidden to wash your hair often - at least 1 time in 3 days.
Mothers newborns note: Stop wrapping your baby up if it's warm enough in a room or outside. Bathe the newborn regularly and in the warm season take a walk outside several times a day. Nursing mothers should not forget about their diet, so that there is no dermatitis, exclude fatty foods.
Complications
As already mentioned, too neglected form of seborrhea leads to its further spread to other areas. If you do not provide medical care in time, the baby may have diarrhea and general malaise. - lethargy, drowsiness or insomnia, loss of appetite and even anemia.
With a weak immunity and the lack of timely treatment to the usual dermatitis infection may be added. Its presence requires medical intervention (pills, injections).
Thus, seborrhea in a child may occur due to various circumstances. If there are yellow scales on the head of the infant, they should simply be eliminated mechanically. With the development of the digestive system and hormonal peeling will disappear by themselves. When, when you suspect dermatitis in older children, seek help from a dermatologist, who will prescribe the correct treatment, setting the root cause.
Causes of dermatitis in children
The main causes of seborrhea in children are:
- The accumulation in the child's body of mother's hormones during the period of pregnancy. Because of their presence, the sebaceous glands function more actively, which leads to the appearance of crusts and spots.
- Genetic heredity.
- Reproduction of yeast fungi Malassezia furfur, caused by various disorders in the child's body. This leads to serious manifestations of the disease and significantly complicates treatment.
- Infectious diseases.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Violations of the gastrointestinal tract.
Other causes of a violation are the following factors:
- defective baby care,
- prolonged stay in the zone of pollution with chemicals, exhaust gases and emissions from industrial enterprises,
- illiterate selection of treatment
- exposure to dyes.

Sometimes the causes of the disease can be several factors in the aggregate. In this case, the treatment will be complex.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Many diseases are very similar in symptoms, pediatric seborrhea is no exception. Therefore, to determine the exact diagnosis of a primary examination specialist may not be enough. It is necessary to make a number of analyzes:
- mycological examination of the skin,
- skin biopsy
- scale microscopy,
- definition of hormonal levels.
They will help identify the cause of seborrhea in a child, and prescribe treatment in accordance with the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment methods depend on the condition of the baby and the cause of the disease.

If seborrhea in a child appears in infants and is caused by the restructuring of the hormonal background, treatment may not be required: closer to 6 months they will disappear on their own. But it must be borne in mind that if the dermatitis is located on the scalp, the seborrheic crust in infants can interfere with the metabolic processes and the normal supply of oxygen to the scalp. To improve the situation, you can take some measures:
- Reconsider the diet of the mother in order to eliminate possible allergens.
- To feed the child is better to choose hypoallergenic mixtures.
- For care, you should use medicated shampoos and creams that regulate salination.
- After the hygiene procedures, you should use the drying means:
- Bioderma,
- Friderm,
- Sulsena.
You can use vegetable oils. To do this, one hour before washing the head, olive oil or special baby oil is applied to the affected skin. A cotton top hat is worn on top. After washing the hair crust need to comb comb with fine teeth. The procedure must be repeated before each swim.
If the cause of the appearance of crusts has become a fungus, you can use special shampoos:

If all treatments fail to produce the desired result, ointments with hormonal ingredients may be given.
Bacterial infection should be treated with antimicrobial agents and drugs to strengthen the immune system.
For the treatment of seborrhea in a child 5 years and older, the use of ointments will be suitable:

If the process has spread to the folds of the skin, use of Castellani fluid is recommended.
The use of folk remedies for the treatment of dermatitis
For those who are afraid to treat the child with medicines, you can use the popular recipes. Seborrheic dermatitis in a child is treated with decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs:
- It is recommended to wipe the affected areas with a decoction of chamomile or sage.
- Good results are also given by lotions of oak bark decoction, prepared in the following ratio: a tablespoon for a glass of water
- You can make an infusion of sage, combined with honey. It can replace itching ointment and healing agents.
These remedies eliminate dandruff, relieve itching, and dry the skin.
Care rules
 In order for the therapy of seborrheic dermatitis in a child to be effective, it is important:
In order for the therapy of seborrheic dermatitis in a child to be effective, it is important:
- wash your baby’s hair regularly
- do not use soap for shampoos intended for adults,
- do not use someone else's towels,
- gently remove the skin from the skin, but do not comb the inflammation (you can carry the infection),
- change bed sheets weekly
- provide regular walks in the fresh air and proper sleep,
- eliminate increased training loads and stresses.
Oak bark decoction
Very good to cope with the disease head decoction of oak bark.
To make it you need to take a spoonful of bark, pour boiling water over it. Then hold in a thermos or protomit in a water bath. Then add here a spoon of honey. The product is rubbed into the scalp. Then wash off with warm water. Done in a day.
How to treat seborrheic dermatitis in children
If the child does not suffer from crusts on the head, dermatitis does not need to be treated. Parents are advised to follow basic hygiene and this is sufficient. But sometimes the course of the disease is complicated. Then a dermatologist is taken for treatment. For newborns create the best conditions - the baby choose clothes made from natural fabrics that will not irritate the skin, have to abandon hats with rough seams.
Prescribed anthelmintic therapy and antimycotic course using proven drugs. It is recommended to go on an antiallergic diet:
- chocolate is excluded from the child’s diet,
- temporarily have to give up nuts,
- honey can be dangerous
- allergic substances found in eggs and fruits, vegetables, red.
If the baby is breastfed, the mother goes on to eat foods rich in zinc, selenium, vitamins A, C, group B. Overdose also can not be allowed, otherwise the skin inflammation in the baby will only increase.
Medicines
Medicines that are prescribed by a dermatologist, are designed to adjust the work of the sebaceous glands of the infant. Thanks to them, crusts and scales move away from the skin faster. If dermatitis is diagnosed in mild form, shampoo, foam, gel will help. As effective drugs, doctors prescribe Friderm, Saforel, Sensibio Bioderma, Mustel Bebe.
Baby soap for cleansing crusts ineffective. Moreover, it strongly dries the dermis. When the crusts soften, they are treated with oil. For these purposes, use sterile sterile oil for children or boiled and cooled olive oil. After lubricating the baby’s head, the mother gently strokes the crusts with a comb and small teeth.
For oily dermatitis, zinc medications are used. They slightly dry the skin, relieve inflammation, swelling. If this treatment turned out to be ineffective, try antifungal, with the help of Miconazole, Nizoral. Good reviews collected applications with keratolytic ointment. In extreme cases, resort to hormone therapy.
What you think about seborrheic dermatitis Komarovsky, you will learn by watching the video:
Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis in babies
Prevention is the best way to avoid long-term treatment. To reduce the likelihood of dermatitis, the following measures are recommended:
- during pregnancy, women need to carefully monitor nutrition,
- the newborn must be provided with care according to all the rules
- with the introduction of complementary foods should consult with a pediatrician and follow his recommendations,
- To care for your baby (especially up to a year), you need to use hypoallergenic cosmetics to prevent the appearance of seborrheic dermatitis in a child,
- when caring for a child should use products made from natural fabrics.
Elementary measures can significantly affect the health of the child and exclude the appearance of certain diseases of the skin.


 decoction of nettle or sage (100 grams of dry raw materials pour 1.5 liters of boiled water, boil in a water bath for 10 minutes, insist for 20 minutes) - used for washing or rinsing the head.
decoction of nettle or sage (100 grams of dry raw materials pour 1.5 liters of boiled water, boil in a water bath for 10 minutes, insist for 20 minutes) - used for washing or rinsing the head.